What are the different image formats JPG, JPEG, GIF, PNG and SVG?
- Tram Ho
On the Internet every day millions of millions of data are transmitted in the form of digital images. JPG, JPEG, GIF, PNG or SVG are the most used image formats on the Internet today. In this article, we will learn about common image formats, know the differences between image formats and in what cases they should be used.
The following infographic will help us better understand the above formats. From the origin of the format, the pronunciation and the method of compressing their data, thereby helping us better understand the properties of each format for each job and appropriate purpose. Let’s find out which file format is most suitable for you!
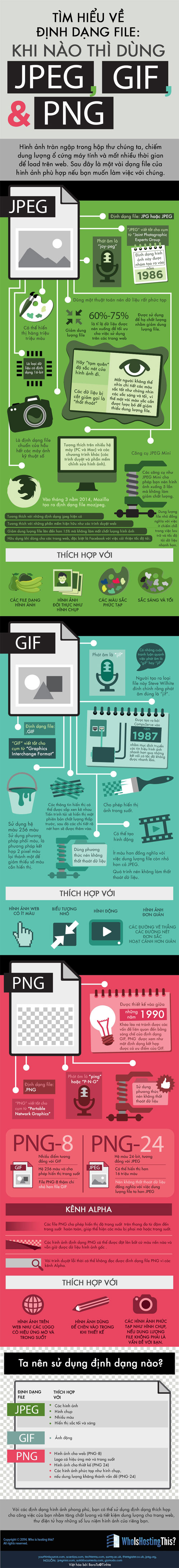
JPG or JPEG image format (Joint Photographic Experts Group)
JPG (original name is JPEG – short for 4 words Joint Photographic Experts Group). There is no difference between JPG and JPEG except that 1 has 3 characters, 1 has 4 characters. Initially, this format was created by Joint Photographic Experts Group, or JPEG for short, but because MS DOS could only handle or read files with a 3-character extension, JPEG was shortened to JPG. . Today JPEG is used to provide a more complete abbreviation for the term Joint Photographic Experts Group. From here, the article will use JPEG.
JPEG is a 16bit image format that can combine red, blue and green light to display millions of colors. This makes JPEG “image friendly” and is the standard format for most digital cameras today.
JPEG allows flexible image compression from 0% (maximum compression) to 100% (no compression). Typically, the JPEG compression setting will be set to 60-75% to significantly reduce image file size but the image will still look good on most screens.
JPEG is a lossy type of compression, so it cannot be used for continuous image editing. Exporting images to JPEG format will reduce quality, and continuous import and export will make the image quality worse. This is why professional photographers often shoot in RAW format so photos don’t lose quality.
JPEG cannot preserve image transparency.
JPEG is commonly used for:
- Still images
- Photography
- Photos with complex colors
GIF image format (Graphic Interchange Format)
GIF is an 8bit color file, it is limited to a palette of up to 256 colors. Basically, every GIF image contains a “pre-set” crayon and there’s no way to actually combine those colors into new colors.
The number 256 colors sounds like a lot, but complex photos often have thousands of tones. This color range is lost during conversion into GIFs and this is the main reason why GIFs are not used for color photographs.
While not a good choice for color images, the 256-color limit can make image files smaller, ideal for situations where the Internet speed is too slow. GIF is a format that maintains image transparency for many years, although PNG and SVG also provide this option.
In addition to support for transparent images, GIF also supports animation, limiting every frame to 256 pre-selected colors. GIF is a compressed format that does not lose data, so it is used to keep straight lines on typography and geometric shapes, whether these objects are suitable for vector graphics files like SVG, or the AI format of Adobe Illustrator.
GIFs are not ideal for modern photography as well as photo storage. When small, GIF images may be smaller than JPEG images due to the limited color palette, but at regular image sizes, JPEG compressed images will produce a smaller image size. GIF images are now quite obsolete, often used to create funny animations or rough transparent images only.
GIF images are used for:
- Simple animation
- Small icon
- Graphics with low pixel-to-pixel variations (flat colors like logos and flags).
PNG image format (Portable Network Graphics)
A newer image format than GIF and JPEG is PNG. PNG is like a “marriage” of GIF and JPEG thanks to the best features of these two image formats. PNG uses the LZW compression algorithm that does not lose image quality, supports transparency so it is a great format for Internet graphics.
PNG supports 8bit color like GIF, but also supports 24bit RGB color like JPEG. PNG belongs to lossless compression, which does not degrade the image. PNG file size is usually larger than JPEG, GIF and is not supported by some browsers (usually older browsers).
- PNG-8: Similar to GIF and uses the same 256-color palette, it supports better transparency options, and usually exports files with a smaller file size, but PNG-8 has no animation function.
- PNG-24: Allows images to be displayed in millions of colors – like JPEG – but provides the ability to preserve transparency. This is also the largest image format, if image quality is more important than image file size, PNG-24 is the best choice for you. If you still care about file size, you can try using TinyPNG.com to compress it.
Compared to JPEG, PNG-24 is not compatible with all applications and platforms, so it is not an ideal format to share on the web. However, if you need to edit photos many times, but do not want to reduce image quality, that’s what PNG can do.
PNG is used for:
- Web graphics require transparency
- Colorful pictures or graphics with high complexity
- Images need to be edited and exported many times
Infographic summary about JPEG, PNG and GIF
SVG (Scalable Vector Graphics) Format
Unlike the above 3 formats, SVG is not a pure bitmap format. It is a vector format – a close relative to EPS (files that can contain text, graphic images, becoming an attractive choice for web and UI designers) and the AI format of Adobe Illustrator. You can think of SVG as “HTML for Illustrator” and need to think of SVG differently from other image formats.
SVG is best suited for displaying logos, icons, maps, flags, charts and other graphics created in vector graphics applications such as Illustrator, Sketch and Inkscape. Written in XML-based markups, SVG files can be edited in any text editor, and can be modified with JavaScript or CSS. Because vectors can be scaled to any size while retaining sharp image quality, they are ideal for responsive designs.
You can embed bitmap graphics into SVG files just like embedding JPEG images into HTML, by linking to the image source via the URL or encapsulating the image as a Data URI. This feature makes SVG more flexible and powerful than other image formats.
Source : Techtalk
