Burndown chart is a popular & easy to use tool for progress management for Scrum teams. A typical burndown chart includes:
- Y axis: shows the total workload that the Scrum Team needs to complete to reach the sprint goal. The normal units of calculation are story points, or estimated man-hours or man-days
- X axis: number of working days in sprint
- Ideal line: expected progress each day to achieve the sprint goal.
- Actual line: Actual progress that Scrum Team achieves through each day
Through monitoring burndown chart, Scrum Team will grasp information such as:
- Amount of work completed in the sprint
- Actual progress is fast or slow compared to ideal progress
- The remaining work needs to be completed to reach the sprint goal
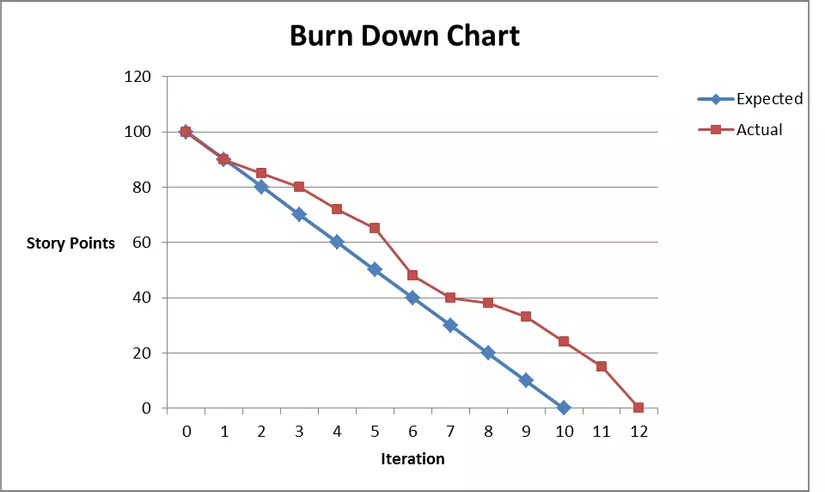
Monitoring progress through the Burndown chart will help Scrum Team detect early risks, problems that may affect the ability to achieve the sprint goal, to come up with plans to handle & improve the situation.
1. Common patterns of Burndown Chart
| Pattern | Explained | What should the Scrum Team do |
|---|---|---|
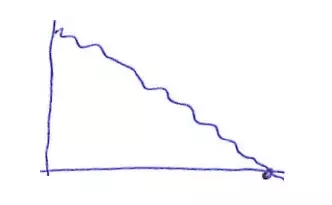 | Ideal pattern of Burndown chart, when the actual line is almost close to the ideal line. The amount of workload is just enough for the team to complete on time, it seems that there is no task completed too soon or too late, progress is updated regularly every day on the management tool. | This is a good pattern, the Scrum Team needs to continue to promote |
 | Pattern represents a mature Scrum Team and good adaptability to achieve the sprint goal. Although there were difficulties in progress at the beginning of the sprint, through adjusting the scope properly, handling difficulties at the right time, speeding up in the last days, the team achieved the target. | If the team completes the sprint goal earlier than the deadline, they may consider adding more work to the sprint |
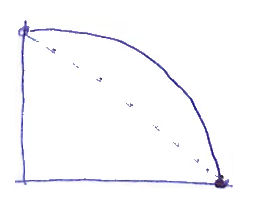 | Patterns that Scrum Teams often encounter. This pattern happens when the team does not complete the workload specified from Sprint Planning, some work may have been moved to a later sprint or moved back to the backlog; However, the team still has certain improvements & adjustments to achieve the ultimate goal of completing the sprint goal | When the burndown chart starts to show signs of following this pattern, the Scrum Team needs to discuss to make the necessary adjustments immediately, such as solving blockers, bringing some low priority tasks out of the sprint, PO considers simple requirements, or the team needs to find other solutions that are simpler and still achieve the set goals |
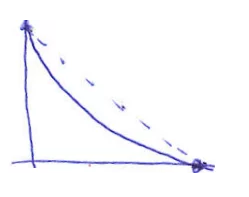 | Pattern shows that the team is completing the task earlier than expected; The cause may be due to the task being overestimated, or the actual team size is larger than when doing planning, or the sprint PO has not created enough workload for the team at the beginning. | It is necessary to have low priority tasks available so that when this pattern appears, the Scrum Team immediately adds these tasks to the sprint, avoiding wasting resources. |
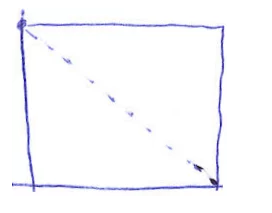 | Pattern signals that the Scrum Team is not voluntarily updating daily progress, or not knowing the definition of done, or the task being overestimated. | Do the Retrospective meeting immediately as soon as the pattern lasts until day 3; performs training session about Scrum practices for Scrum Team |
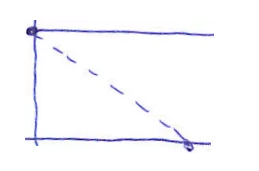 | Similar to the previous pattern, this pattern shows that the Scrum Team is not understanding & not working according to Scrum practices | Perform Scrum training & Retrospective as soon as possible |
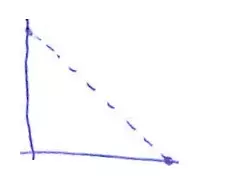 | The task is not estimated at a Sprint planning meeting; or the backlog is currently empty because there is no request from the PO or has not been updated | Stop sprint, implement estimate of tasks & re-update backlog. Restart sprint when the tasks have been completely updated |
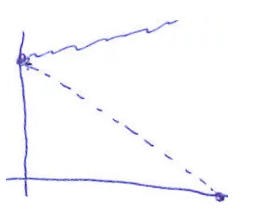 | Pattern shows a sign of persistent new tasks added to sprints after Sprint Planning, or initial tasks themselves that have been underestimated & team is estimating; With this pattern, the team cannot complete the sprint goal | Reserve a full session to estimate the tasks in the backlog. If the initial sprint goal cannot be completed in a sprint, or doesn’t make sense anymore, consider stopping the sprint & restarting a new sprint. |
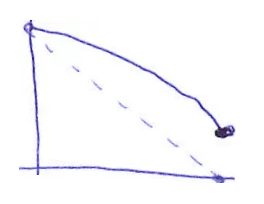 | Pattern shows that the team did not complete the sprint goal on time; The cause may be due to the underestimate task, the velocity did not meet the expectations, or the lack of the necessary adjustments when faced with risks, problems arise. | When detecting a potentially unsuccessful sprint goal, it is necessary to remove the low priority tasks from the sprint, and focus on solving the arising problems, suggesting alternative options to achieve the sprint goal. |
 | Pattern shows that the team is completing the sprint goal earlier than expected; The cause may be due to the task being overestimated, the team committed to a little work, the velocity was miscalculated, or the team didn’t have enough workload to perform | It is necessary to have low priority tasks available so that when this pattern appears, the Scrum Team immediately adds these tasks to the sprint, avoiding wasting resources. |
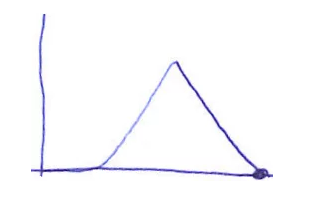 | Pattern shows that estimation of the task is not carried out during a sprint planning session, but until mid-sprint team will have tasks, or at this time the task will have estimation; The reason may be that PO did not prepare the task in time, or the team lacked information, could not complete the estimate in a sprint planning meeting. | This pattern should not be allowed to happen, it should be ensured that the task is ready to estimate & include in a sprint backlog before a sprint planning |
2. Advantages and disadvantages when using Burndown Chart
Advantages
- Simple, easy to use
- Make it clear what the Scrum Team needs to achieve, and what has been achieved
- Show off whether the Scrum Team is on track
- Early warning to the Scrum Team about problems that arise, bottlenecks that need to be solved immediately
- The direction the Scrum Team needs to focus on to achieve its goal
- Motivate Scrum Team spirit
Defect
- Information shown is limited, showing only part of the big picture
- Show only completed or incomplete tasks (done vs not done); not showing the progress of tasks in progress (in progress)
- May lead to unrealistic expectations of the Scrum Team’s workload completion (due to the lack of information to evaluate, lack of data on dependencies, risks, etc.)
Source : https://luis-goncalves.com/burndown-chart-ultimate-guide/ https://www.scrumdesk.com/is-it-your-burn-down-chart/
