1. Introduction
In the previous post Chrome Extension: Getting Started, I have introduced what chrome extension is and how to write a small but very useful chrome extension. In this post, we’re gonna up our game a little bit by writing a more complex chrome extension. The final extension will look like this:
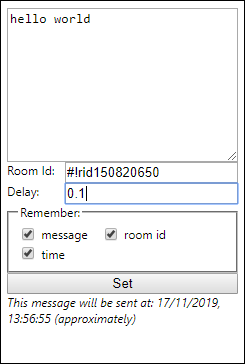
This extension will help us to automatically send a certain message to a certain room of the Chatwork website. The full
source code can be found here: https://github.com/nguyenyou0812/auto-send-message
2. Key concepts
2.1. chrome.browserAction
Use browser actions to put icons in the main Google Chrome toolbar, to the right of the address bar. In addition to its icon, a browser action can have a tooltip, a badge, and a popup.
If a browser action has a popup, the popup appears when the user clicks the icon. The popup can contain any HTML contents that you like, and it’s automatically sized to fit its contents.
To add a popup to your browser action, create an HTML file with the popup’s contents. Specify the HTML file in the default_popup field of browser_action in the manifest, or call the browserAction.setPopup method.
2.2. Content Scripts
Content scripts are files that run in the context of web pages. By using the standard Document Object Model (DOM), they are able to read details of the web pages the browser visits, make changes to them and pass information to their parent extension.
Content scripts can access Chrome APIs used by their parent extension by exchanging messages with the extension. They can also access the URL of an extension’s file with chrome.runtime.getURL() and use the result the same as other URLs.
2.3. Chrome.tabs
Use the chrome.tabs API to interact with the browser’s tab system. You can use this API to create, modify, and rearrange tabs in the browser.
u can use most chrome.tabs methods and events without declaring any permissions in the extension’s manifest file. However, if you require access to the url, pendingUrl, title, or favIconUrl properties of tabs.Tab, you must declare the “tabs” permission in the manifest
3. Implementation
Creating a folder named AuSeMe and adding the following files. After that, loading this extension in chrome extension developer mode.
1 2 3 4 5 6 | AuSeMe │--manifest.json │--contentScript.js │--popup.html │--popup.js |
manifest.json
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 | <span class="token punctuation">{</span> <span class="token property">"manifest_version"</span><span class="token operator">:</span> <span class="token number">2</span><span class="token punctuation">,</span> <span class="token property">"name"</span><span class="token operator">:</span> <span class="token string">"Auto Send Message"</span><span class="token punctuation">,</span> <span class="token property">"version"</span><span class="token operator">:</span> <span class="token string">"2.0"</span><span class="token punctuation">,</span> <span class="token property">"content_scripts"</span><span class="token operator">:</span> <span class="token punctuation">[</span> <span class="token punctuation">{</span> <span class="token property">"matches"</span><span class="token operator">:</span> <span class="token punctuation">[</span><span class="token string">"https://www.chatwork.com/*"</span><span class="token punctuation">]</span><span class="token punctuation">,</span> <span class="token property">"js"</span><span class="token operator">:</span> <span class="token punctuation">[</span><span class="token string">"contentScript.js"</span><span class="token punctuation">]</span> <span class="token punctuation">}</span> <span class="token punctuation">]</span><span class="token punctuation">,</span> <span class="token property">"permissions"</span><span class="token operator">:</span> <span class="token punctuation">[</span><span class="token string">"tabs"</span><span class="token punctuation">,</span> <span class="token string">"storage"</span><span class="token punctuation">]</span><span class="token punctuation">,</span> <span class="token property">"browser_action"</span><span class="token operator">:</span> <span class="token punctuation">{</span> <span class="token property">"default_popup"</span><span class="token operator">:</span> <span class="token string">"popup.html"</span><span class="token punctuation">,</span> <span class="token property">"default_title"</span><span class="token operator">:</span> <span class="token string">"Auto send message popup"</span> <span class="token punctuation">}</span> <span class="token punctuation">}</span> |
popup.html
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 | <span class="token tag"><span class="token tag"><span class="token punctuation"><</span>html</span><span class="token punctuation">></span></span> <span class="token tag"><span class="token tag"><span class="token punctuation"><</span>head</span><span class="token punctuation">></span></span> <span class="token tag"><span class="token tag"><span class="token punctuation"><</span>style</span><span class="token punctuation">></span></span><span class="token style language-css"> <span class="token selector">.clearfix::after</span> <span class="token punctuation">{</span> <span class="token property">content</span><span class="token punctuation">:</span> <span class="token string">""</span><span class="token punctuation">;</span> <span class="token property">clear</span><span class="token punctuation">:</span> both<span class="token punctuation">;</span> <span class="token property">display</span><span class="token punctuation">:</span> table<span class="token punctuation">;</span> <span class="token punctuation">}</span> <span class="token selector">.f-right</span> <span class="token punctuation">{</span> <span class="token property">float</span><span class="token punctuation">:</span> right <span class="token punctuation">}</span> <span class="token selector">.checkboxes label</span> <span class="token punctuation">{</span> <span class="token property">display</span><span class="token punctuation">:</span> inline-block<span class="token punctuation">;</span> <span class="token property">padding-right</span><span class="token punctuation">:</span> 10px<span class="token punctuation">;</span> <span class="token property">white-space</span><span class="token punctuation">:</span> nowrap<span class="token punctuation">;</span> <span class="token punctuation">}</span> <span class="token selector">.checkboxes input</span> <span class="token punctuation">{</span> <span class="token property">vertical-align</span><span class="token punctuation">:</span> middle<span class="token punctuation">;</span> <span class="token punctuation">}</span> <span class="token selector">.checkboxes label span</span> <span class="token punctuation">{</span> <span class="token property">vertical-align</span><span class="token punctuation">:</span> middle<span class="token punctuation">;</span> <span class="token punctuation">}</span> </span><span class="token tag"><span class="token tag"><span class="token punctuation"></</span>style</span><span class="token punctuation">></span></span> <span class="token tag"><span class="token tag"><span class="token punctuation"></</span>head</span><span class="token punctuation">></span></span> <span class="token tag"><span class="token tag"><span class="token punctuation"><</span>body</span><span class="token punctuation">></span></span> <span class="token tag"><span class="token tag"><span class="token punctuation"><</span>textarea</span> <span class="token attr-name">id</span><span class="token attr-value"><span class="token punctuation">=</span><span class="token punctuation">"</span>chatText<span class="token punctuation">"</span></span> <span class="token attr-name">cols</span><span class="token attr-value"><span class="token punctuation">=</span><span class="token punctuation">"</span>30<span class="token punctuation">"</span></span> <span class="token attr-name">rows</span><span class="token attr-value"><span class="token punctuation">=</span><span class="token punctuation">"</span>10<span class="token punctuation">"</span></span> <span class="token attr-name">placeholder</span><span class="token attr-value"><span class="token punctuation">=</span><span class="token punctuation">"</span>chat message<span class="token punctuation">"</span></span><span class="token punctuation">></span></span><span class="token tag"><span class="token tag"><span class="token punctuation"></</span>textarea</span><span class="token punctuation">></span></span> <span class="token tag"><span class="token tag"><span class="token punctuation"><</span>div</span> <span class="token attr-name">class</span><span class="token attr-value"><span class="token punctuation">=</span><span class="token punctuation">"</span>clearfix<span class="token punctuation">"</span></span><span class="token punctuation">></span></span> Room Id: <span class="token tag"><span class="token tag"><span class="token punctuation"><</span>input</span> <span class="token attr-name">class</span><span class="token attr-value"><span class="token punctuation">=</span><span class="token punctuation">"</span>f-right<span class="token punctuation">"</span></span> <span class="token attr-name">id</span><span class="token attr-value"><span class="token punctuation">=</span><span class="token punctuation">"</span>roomId<span class="token punctuation">"</span></span> <span class="token attr-name">placeholder</span><span class="token attr-value"><span class="token punctuation">=</span><span class="token punctuation">"</span>chat room id<span class="token punctuation">"</span></span> <span class="token attr-name">title</span><span class="token attr-value"><span class="token punctuation">=</span><span class="token punctuation">"</span>e.g. #!rid000000000<span class="token punctuation">"</span></span><span class="token punctuation">/></span></span> <span class="token tag"><span class="token tag"><span class="token punctuation"></</span>div</span><span class="token punctuation">></span></span> <span class="token tag"><span class="token tag"><span class="token punctuation"><</span>div</span> <span class="token attr-name">class</span><span class="token attr-value"><span class="token punctuation">=</span><span class="token punctuation">"</span>clearfix<span class="token punctuation">"</span></span><span class="token punctuation">></span></span> Delay: <span class="token tag"><span class="token tag"><span class="token punctuation"><</span>input</span> <span class="token attr-name">class</span><span class="token attr-value"><span class="token punctuation">=</span><span class="token punctuation">"</span>f-right<span class="token punctuation">"</span></span> <span class="token attr-name">id</span><span class="token attr-value"><span class="token punctuation">=</span><span class="token punctuation">"</span>delayTime<span class="token punctuation">"</span></span> <span class="token attr-name">title</span><span class="token attr-value"><span class="token punctuation">=</span><span class="token punctuation">"</span>default value: 0<span class="token punctuation">"</span></span> <span class="token attr-name">placeholder</span><span class="token attr-value"><span class="token punctuation">=</span><span class="token punctuation">"</span>delay time (minutes)<span class="token punctuation">"</span></span><span class="token punctuation">></span></span> <span class="token tag"><span class="token tag"><span class="token punctuation"></</span>div</span><span class="token punctuation">></span></span> <span class="token tag"><span class="token tag"><span class="token punctuation"><</span>div</span><span class="token punctuation">></span></span> <span class="token tag"><span class="token tag"><span class="token punctuation"><</span>fieldset</span><span class="token style-attr language-css"><span class="token attr-name"> <span class="token attr-name">style</span></span><span class="token punctuation">="</span><span class="token attr-value"><span class="token property">margin-right</span><span class="token punctuation">:</span> 0<span class="token punctuation">;</span> <span class="token property">margin-left</span><span class="token punctuation">:</span> 0</span><span class="token punctuation">"</span></span><span class="token punctuation">></span></span> <span class="token tag"><span class="token tag"><span class="token punctuation"><</span>legend</span><span class="token punctuation">></span></span>Remember:<span class="token tag"><span class="token tag"><span class="token punctuation"></</span>legend</span><span class="token punctuation">></span></span> <span class="token tag"><span class="token tag"><span class="token punctuation"><</span>div</span> <span class="token attr-name">class</span><span class="token attr-value"><span class="token punctuation">=</span><span class="token punctuation">"</span>checkboxes<span class="token punctuation">"</span></span><span class="token punctuation">></span></span> <span class="token tag"><span class="token tag"><span class="token punctuation"><</span>label</span> <span class="token attr-name">for</span><span class="token attr-value"><span class="token punctuation">=</span><span class="token punctuation">"</span>rememberText<span class="token punctuation">"</span></span><span class="token punctuation">></span></span><span class="token tag"><span class="token tag"><span class="token punctuation"><</span>input</span> <span class="token attr-name">type</span><span class="token attr-value"><span class="token punctuation">=</span><span class="token punctuation">"</span>checkbox<span class="token punctuation">"</span></span> <span class="token attr-name">id</span><span class="token attr-value"><span class="token punctuation">=</span><span class="token punctuation">"</span>rememberText<span class="token punctuation">"</span></span> <span class="token punctuation">/></span></span> <span class="token tag"><span class="token tag"><span class="token punctuation"><</span>span</span><span class="token punctuation">></span></span>message<span class="token tag"><span class="token tag"><span class="token punctuation"></</span>span</span><span class="token punctuation">></span></span><span class="token tag"><span class="token tag"><span class="token punctuation"></</span>label</span><span class="token punctuation">></span></span> <span class="token tag"><span class="token tag"><span class="token punctuation"><</span>label</span> <span class="token attr-name">for</span><span class="token attr-value"><span class="token punctuation">=</span><span class="token punctuation">"</span>rememberId<span class="token punctuation">"</span></span><span class="token punctuation">></span></span><span class="token tag"><span class="token tag"><span class="token punctuation"><</span>input</span> <span class="token attr-name">type</span><span class="token attr-value"><span class="token punctuation">=</span><span class="token punctuation">"</span>checkbox<span class="token punctuation">"</span></span> <span class="token attr-name">id</span><span class="token attr-value"><span class="token punctuation">=</span><span class="token punctuation">"</span>rememberId<span class="token punctuation">"</span></span> <span class="token punctuation">/></span></span> <span class="token tag"><span class="token tag"><span class="token punctuation"><</span>span</span><span class="token punctuation">></span></span>room id<span class="token tag"><span class="token tag"><span class="token punctuation"></</span>span</span><span class="token punctuation">></span></span><span class="token tag"><span class="token tag"><span class="token punctuation"></</span>label</span><span class="token punctuation">></span></span> <span class="token tag"><span class="token tag"><span class="token punctuation"><</span>label</span> <span class="token attr-name">for</span><span class="token attr-value"><span class="token punctuation">=</span><span class="token punctuation">"</span>rememberTime<span class="token punctuation">"</span></span><span class="token punctuation">></span></span><span class="token tag"><span class="token tag"><span class="token punctuation"><</span>input</span> <span class="token attr-name">type</span><span class="token attr-value"><span class="token punctuation">=</span><span class="token punctuation">"</span>checkbox<span class="token punctuation">"</span></span> <span class="token attr-name">id</span><span class="token attr-value"><span class="token punctuation">=</span><span class="token punctuation">"</span>rememberTime<span class="token punctuation">"</span></span> <span class="token punctuation">/></span></span> <span class="token tag"><span class="token tag"><span class="token punctuation"><</span>span</span><span class="token punctuation">></span></span>time<span class="token tag"><span class="token tag"><span class="token punctuation"></</span>span</span><span class="token punctuation">></span></span><span class="token tag"><span class="token tag"><span class="token punctuation"></</span>label</span><span class="token punctuation">></span></span> <span class="token tag"><span class="token tag"><span class="token punctuation"></</span>div</span><span class="token punctuation">></span></span> <span class="token tag"><span class="token tag"><span class="token punctuation"></</span>fieldset</span><span class="token punctuation">></span></span> <span class="token tag"><span class="token tag"><span class="token punctuation"></</span>div</span><span class="token punctuation">></span></span> <span class="token tag"><span class="token tag"><span class="token punctuation"><</span>button</span><span class="token style-attr language-css"><span class="token attr-name"> <span class="token attr-name">style</span></span><span class="token punctuation">="</span><span class="token attr-value"><span class="token property">width</span><span class="token punctuation">:</span> 100%</span><span class="token punctuation">"</span></span> <span class="token attr-name">id</span><span class="token attr-value"><span class="token punctuation">=</span><span class="token punctuation">"</span>btnSet<span class="token punctuation">"</span></span><span class="token punctuation">></span></span>Set<span class="token tag"><span class="token tag"><span class="token punctuation"></</span>button</span><span class="token punctuation">></span></span> <span class="token tag"><span class="token tag"><span class="token punctuation"><</span>div</span><span class="token style-attr language-css"><span class="token attr-name"> <span class="token attr-name">style</span></span><span class="token punctuation">="</span><span class="token attr-value"><span class="token property">font-style</span><span class="token punctuation">:</span>italic</span><span class="token punctuation">"</span></span> <span class="token attr-name">id</span><span class="token attr-value"><span class="token punctuation">=</span><span class="token punctuation">"</span>calTime<span class="token punctuation">"</span></span><span class="token punctuation">></span></span><span class="token tag"><span class="token tag"><span class="token punctuation"></</span>div</span><span class="token punctuation">></span></span> <span class="token tag"><span class="token tag"><span class="token punctuation"><</span>script</span> <span class="token attr-name">src</span><span class="token attr-value"><span class="token punctuation">=</span><span class="token punctuation">"</span>popup.js<span class="token punctuation">"</span></span> <span class="token attr-name">type</span><span class="token attr-value"><span class="token punctuation">=</span><span class="token punctuation">"</span>text/javascript<span class="token punctuation">"</span></span><span class="token punctuation">></span></span><span class="token tag"><span class="token tag"><span class="token punctuation"></</span>script</span><span class="token punctuation">></span></span> <span class="token tag"><span class="token tag"><span class="token punctuation"></</span>body</span><span class="token punctuation">></span></span> <span class="token tag"><span class="token tag"><span class="token punctuation"></</span>html</span><span class="token punctuation">></span></span> |
popup.js
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 | <span class="token keyword">let</span> chatText <span class="token operator">=</span> document<span class="token punctuation">.</span><span class="token function">getElementById</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span><span class="token string">'chatText'</span><span class="token punctuation">)</span> <span class="token keyword">let</span> delayTime <span class="token operator">=</span> document<span class="token punctuation">.</span><span class="token function">getElementById</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span><span class="token string">'delayTime'</span><span class="token punctuation">)</span> <span class="token keyword">let</span> roomId <span class="token operator">=</span> document<span class="token punctuation">.</span><span class="token function">getElementById</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span><span class="token string">'roomId'</span><span class="token punctuation">)</span> <span class="token keyword">let</span> button <span class="token operator">=</span> document<span class="token punctuation">.</span><span class="token function">getElementById</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span><span class="token string">'btnSet'</span><span class="token punctuation">)</span> <span class="token keyword">let</span> chboxText <span class="token operator">=</span> document<span class="token punctuation">.</span><span class="token function">getElementById</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span><span class="token string">'rememberText'</span><span class="token punctuation">)</span> <span class="token keyword">let</span> chboxId <span class="token operator">=</span> document<span class="token punctuation">.</span><span class="token function">getElementById</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span><span class="token string">'rememberId'</span><span class="token punctuation">)</span> <span class="token keyword">let</span> chboxTime <span class="token operator">=</span> document<span class="token punctuation">.</span><span class="token function">getElementById</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span><span class="token string">'rememberTime'</span><span class="token punctuation">)</span> delayTime<span class="token punctuation">.</span><span class="token function">addEventListener</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span><span class="token string">'input'</span><span class="token punctuation">,</span> updateValue<span class="token punctuation">)</span><span class="token punctuation">;</span> button<span class="token punctuation">.</span><span class="token function">addEventListener</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span><span class="token string">'click'</span><span class="token punctuation">,</span> setAction<span class="token punctuation">)</span> chrome<span class="token punctuation">.</span>storage<span class="token punctuation">.</span>sync<span class="token punctuation">.</span><span class="token keyword">get</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span><span class="token punctuation">[</span><span class="token string">'rid'</span><span class="token punctuation">,</span><span class="token string">'txt'</span><span class="token punctuation">,</span><span class="token string">'tme'</span><span class="token punctuation">,</span><span class="token string">'cid'</span><span class="token punctuation">,</span><span class="token string">'ctxt'</span><span class="token punctuation">,</span><span class="token string">'ctme'</span><span class="token punctuation">]</span><span class="token punctuation">,</span> <span class="token keyword">function</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span>obj<span class="token punctuation">)</span> <span class="token punctuation">{</span> roomId<span class="token punctuation">.</span>value <span class="token operator">=</span> obj<span class="token punctuation">.</span>rid <span class="token operator">?</span> obj<span class="token punctuation">.</span>rid <span class="token punctuation">:</span> <span class="token string">''</span> chatText<span class="token punctuation">.</span>value <span class="token operator">=</span> obj<span class="token punctuation">.</span>txt <span class="token operator">?</span> obj<span class="token punctuation">.</span>txt <span class="token punctuation">:</span> <span class="token string">''</span> delayTime<span class="token punctuation">.</span>value <span class="token operator">=</span> obj<span class="token punctuation">.</span>tme <span class="token operator">?</span> obj<span class="token punctuation">.</span>tme <span class="token punctuation">:</span> <span class="token string">''</span> chboxId<span class="token punctuation">.</span>checked <span class="token operator">=</span> obj<span class="token punctuation">.</span>cid chboxText<span class="token punctuation">.</span>checked <span class="token operator">=</span> obj<span class="token punctuation">.</span>ctxt chboxTime<span class="token punctuation">.</span>checked <span class="token operator">=</span> obj<span class="token punctuation">.</span>ctme <span class="token punctuation">}</span><span class="token punctuation">)</span><span class="token punctuation">;</span> <span class="token keyword">function</span> <span class="token function">addMinutes</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span>date<span class="token punctuation">,</span> minutes<span class="token punctuation">)</span> <span class="token punctuation">{</span> <span class="token keyword">return</span> <span class="token keyword">new</span> <span class="token class-name">Date</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span>date<span class="token punctuation">.</span><span class="token function">getTime</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span><span class="token punctuation">)</span> <span class="token operator">+</span> minutes<span class="token operator">*</span><span class="token number">60000</span><span class="token punctuation">)</span><span class="token punctuation">;</span> <span class="token punctuation">}</span> <span class="token keyword">function</span> <span class="token function">updateValue</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span>e<span class="token punctuation">)</span> <span class="token punctuation">{</span> <span class="token keyword">const</span> tme <span class="token operator">=</span> <span class="token function">parseFloat</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span>e<span class="token punctuation">.</span>target<span class="token punctuation">.</span>value<span class="token punctuation">)</span> <span class="token keyword">let</span> end <span class="token operator">=</span> <span class="token function">addMinutes</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span><span class="token keyword">new</span> <span class="token class-name">Date</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span><span class="token punctuation">)</span><span class="token punctuation">,</span> tme<span class="token punctuation">)</span> calTime<span class="token punctuation">.</span>innerHTML <span class="token operator">=</span> <span class="token template-string"><span class="token string">`This message will be sent at: </span><span class="token interpolation"><span class="token interpolation-punctuation punctuation">${</span>end<span class="token punctuation">.</span><span class="token function">toLocaleString</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span><span class="token string">'en-GB'</span><span class="token punctuation">)</span><span class="token interpolation-punctuation punctuation">}</span></span><span class="token string"> (approximately)`</span></span> <span class="token punctuation">}</span> <span class="token keyword">function</span> <span class="token function">setAction</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span><span class="token punctuation">)</span> <span class="token punctuation">{</span> <span class="token keyword">let</span> txt <span class="token operator">=</span> chatText<span class="token punctuation">.</span>value<span class="token punctuation">.</span><span class="token function">trim</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span><span class="token punctuation">)</span> <span class="token keyword">let</span> tme <span class="token operator">=</span> <span class="token function">parseFloat</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span>delayTime<span class="token punctuation">.</span>value<span class="token punctuation">.</span><span class="token function">trim</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span><span class="token punctuation">)</span><span class="token punctuation">)</span> <span class="token keyword">let</span> rid <span class="token operator">=</span> roomId<span class="token punctuation">.</span>value<span class="token punctuation">.</span><span class="token function">trim</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span><span class="token punctuation">)</span> <span class="token keyword">if</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span>txt<span class="token punctuation">.</span>length <span class="token operator">></span> <span class="token number">255</span><span class="token punctuation">)</span> <span class="token punctuation">{</span> txt <span class="token operator">=</span> txt<span class="token punctuation">.</span><span class="token function">substring</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span><span class="token number">0</span><span class="token punctuation">,</span> <span class="token number">256</span><span class="token punctuation">)</span> <span class="token punctuation">}</span> <span class="token keyword">if</span> <span class="token punctuation">(</span><span class="token function">isNaN</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span>tme<span class="token punctuation">)</span><span class="token punctuation">)</span> <span class="token punctuation">{</span> tme <span class="token operator">=</span> <span class="token number">0</span> delayTime<span class="token punctuation">.</span>value <span class="token operator">=</span> tme <span class="token punctuation">}</span> <span class="token keyword">const</span> regex <span class="token operator">=</span> <span class="token regex">/^#!rid[0-9]{8,9}$/</span> <span class="token keyword">if</span> <span class="token punctuation">(</span><span class="token operator">!</span>regex<span class="token punctuation">.</span><span class="token function">test</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span>rid<span class="token punctuation">)</span><span class="token punctuation">)</span> <span class="token punctuation">{</span> <span class="token function">alert</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span><span class="token string">'Invalid Room Id'</span><span class="token punctuation">)</span> <span class="token keyword">return</span> <span class="token punctuation">}</span> <span class="token keyword">const</span> payload <span class="token operator">=</span> <span class="token punctuation">{</span> rid<span class="token punctuation">:</span> chboxId<span class="token punctuation">.</span>checked <span class="token operator">?</span> rid <span class="token punctuation">:</span> <span class="token keyword">null</span><span class="token punctuation">,</span> txt<span class="token punctuation">:</span> chboxText<span class="token punctuation">.</span>checked <span class="token operator">?</span> txt<span class="token punctuation">:</span> <span class="token keyword">null</span><span class="token punctuation">,</span> tme<span class="token punctuation">:</span> chboxTime<span class="token punctuation">.</span>checked <span class="token operator">?</span> tme<span class="token punctuation">:</span> <span class="token keyword">null</span><span class="token punctuation">,</span> cid<span class="token punctuation">:</span> chboxId<span class="token punctuation">.</span>checked <span class="token operator">?</span> <span class="token boolean">true</span> <span class="token punctuation">:</span> <span class="token boolean">false</span><span class="token punctuation">,</span> ctxt<span class="token punctuation">:</span> chboxText<span class="token punctuation">.</span>checked <span class="token operator">?</span> <span class="token boolean">true</span> <span class="token punctuation">:</span> <span class="token boolean">false</span><span class="token punctuation">,</span> ctme<span class="token punctuation">:</span> chboxTime<span class="token punctuation">.</span>checked <span class="token operator">?</span> <span class="token boolean">true</span><span class="token punctuation">:</span> <span class="token boolean">false</span> <span class="token punctuation">}</span> chrome<span class="token punctuation">.</span>storage<span class="token punctuation">.</span>sync<span class="token punctuation">.</span><span class="token keyword">set</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span>payload<span class="token punctuation">)</span><span class="token punctuation">;</span> <span class="token keyword">let</span> end <span class="token operator">=</span> <span class="token function">addMinutes</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span><span class="token keyword">new</span> <span class="token class-name">Date</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span><span class="token punctuation">)</span><span class="token punctuation">,</span> tme<span class="token punctuation">)</span> calTime<span class="token punctuation">.</span>innerHTML <span class="token operator">=</span> <span class="token template-string"><span class="token string">`This message will be sent at: </span><span class="token interpolation"><span class="token interpolation-punctuation punctuation">${</span>end<span class="token punctuation">.</span><span class="token function">toLocaleString</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span><span class="token string">'en-GB'</span><span class="token punctuation">)</span><span class="token interpolation-punctuation punctuation">}</span></span><span class="token string"> (approximately)`</span></span> chrome<span class="token punctuation">.</span>tabs<span class="token punctuation">.</span><span class="token function">query</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span><span class="token punctuation">{</span>active<span class="token punctuation">:</span> <span class="token boolean">true</span><span class="token punctuation">,</span> currentWindow<span class="token punctuation">:</span> <span class="token boolean">true</span><span class="token punctuation">}</span><span class="token punctuation">,</span> <span class="token keyword">function</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span>tabs<span class="token punctuation">)</span> <span class="token punctuation">{</span> <span class="token keyword">if</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span><span class="token operator">!</span>tabs<span class="token punctuation">[</span><span class="token number">0</span><span class="token punctuation">]</span><span class="token punctuation">.</span>url<span class="token punctuation">.</span><span class="token function">includes</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span><span class="token string">'https://www.chatwork.com'</span><span class="token punctuation">)</span><span class="token punctuation">)</span> <span class="token punctuation">{</span> <span class="token function">alert</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span><span class="token string">'please go to https://www.chatwork.com'</span><span class="token punctuation">)</span> <span class="token keyword">return</span> <span class="token punctuation">}</span> <span class="token keyword">const</span> payload <span class="token operator">=</span> <span class="token punctuation">{</span> txt<span class="token punctuation">,</span> tme<span class="token punctuation">,</span> rid <span class="token punctuation">}</span> chrome<span class="token punctuation">.</span>tabs<span class="token punctuation">.</span><span class="token function">sendMessage</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span>tabs<span class="token punctuation">[</span><span class="token number">0</span><span class="token punctuation">]</span><span class="token punctuation">.</span>id<span class="token punctuation">,</span> payload<span class="token punctuation">)</span><span class="token punctuation">;</span> <span class="token punctuation">}</span><span class="token punctuation">)</span><span class="token punctuation">;</span> <span class="token punctuation">}</span> |
contentScript.js
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 | <span class="token keyword">function</span> <span class="token function">simulateChat</span> <span class="token punctuation">(</span>content<span class="token punctuation">)</span> <span class="token punctuation">{</span> <span class="token keyword">let</span> input <span class="token operator">=</span> document<span class="token punctuation">.</span><span class="token function">getElementById</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span><span class="token string">'_chatText'</span><span class="token punctuation">)</span> <span class="token keyword">if</span> <span class="token punctuation">(</span>input<span class="token punctuation">)</span> <span class="token punctuation">{</span> <span class="token keyword">let</span> nativeInputValueSetter <span class="token operator">=</span> Object<span class="token punctuation">.</span><span class="token function">getOwnPropertyDescriptor</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span>window<span class="token punctuation">.</span>HTMLTextAreaElement<span class="token punctuation">.</span>prototype<span class="token punctuation">,</span> <span class="token string">"value"</span><span class="token punctuation">)</span><span class="token punctuation">.</span><span class="token keyword">set</span><span class="token punctuation">;</span> nativeInputValueSetter<span class="token punctuation">.</span><span class="token function">call</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span>input<span class="token punctuation">,</span> content<span class="token punctuation">)</span><span class="token punctuation">;</span> <span class="token keyword">let</span> ev <span class="token operator">=</span> <span class="token keyword">new</span> <span class="token class-name">Event</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span><span class="token string">'input'</span><span class="token punctuation">,</span> <span class="token punctuation">{</span> bubbles<span class="token punctuation">:</span> <span class="token boolean">true</span><span class="token punctuation">}</span><span class="token punctuation">)</span><span class="token punctuation">;</span> input<span class="token punctuation">.</span><span class="token function">dispatchEvent</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span>ev<span class="token punctuation">)</span><span class="token punctuation">;</span> <span class="token keyword">let</span> button <span class="token operator">=</span> document<span class="token punctuation">.</span><span class="token function">getElementsByClassName</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span><span class="token string">'sc-kasBVs chatInput__submit dOfbLu'</span><span class="token punctuation">)</span><span class="token punctuation">[</span><span class="token number">0</span><span class="token punctuation">]</span> <span class="token function">setTimeout</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span><span class="token punctuation">)</span> <span class="token operator">=></span> <span class="token punctuation">{</span> button<span class="token punctuation">.</span><span class="token function">click</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span><span class="token punctuation">)</span> <span class="token punctuation">}</span><span class="token punctuation">,</span> <span class="token number">500</span><span class="token punctuation">)</span> <span class="token punctuation">}</span> <span class="token punctuation">}</span> <span class="token keyword">function</span> <span class="token function">autoChat</span> <span class="token punctuation">(</span>minute<span class="token punctuation">,</span> content<span class="token punctuation">,</span> rid<span class="token punctuation">)</span> <span class="token punctuation">{</span> <span class="token keyword">const</span> time <span class="token operator">=</span> minute <span class="token operator">*</span> <span class="token number">60</span> <span class="token operator">*</span> <span class="token number">1000</span> <span class="token function">setTimeout</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span><span class="token punctuation">)</span> <span class="token operator">=></span> <span class="token punctuation">{</span> <span class="token keyword">if</span> <span class="token punctuation">(</span>rid<span class="token punctuation">)</span> <span class="token punctuation">{</span> window<span class="token punctuation">.</span>location<span class="token punctuation">.</span>href <span class="token operator">=</span> <span class="token template-string"><span class="token string">`https://www.chatwork.com/</span><span class="token interpolation"><span class="token interpolation-punctuation punctuation">${</span>rid<span class="token interpolation-punctuation punctuation">}</span></span><span class="token string">`</span></span> <span class="token punctuation">}</span> <span class="token function">setTimeout</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span><span class="token punctuation">)</span> <span class="token operator">=></span> <span class="token punctuation">{</span> <span class="token function">simulateChat</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span>content<span class="token punctuation">)</span> <span class="token punctuation">}</span><span class="token punctuation">,</span> rid <span class="token operator">?</span> <span class="token number">500</span> <span class="token punctuation">:</span> <span class="token number">0</span><span class="token punctuation">)</span> <span class="token punctuation">}</span><span class="token punctuation">,</span> time<span class="token punctuation">)</span> <span class="token punctuation">}</span> chrome<span class="token punctuation">.</span>runtime<span class="token punctuation">.</span>onMessage<span class="token punctuation">.</span><span class="token function">addListener</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span>gotMessage<span class="token punctuation">)</span> <span class="token keyword">function</span> <span class="token function">gotMessage</span> <span class="token punctuation">(</span>message<span class="token punctuation">,</span> sender<span class="token punctuation">,</span> sendResponse<span class="token punctuation">)</span> <span class="token punctuation">{</span> <span class="token function">autoChat</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span>message<span class="token punctuation">.</span>tme<span class="token punctuation">,</span> message<span class="token punctuation">.</span>txt<span class="token punctuation">,</span> message<span class="token punctuation">.</span>rid<span class="token punctuation">)</span> <span class="token punctuation">}</span> |
4. Conclusion
In this post, I just showed you how to communicate between the popup and the content script by using Message Passing technique. Hopefully, this small tutorial will give you some ideas about how to connect the available chrome extension components and also inspire you to write many more big, power chrome extensions.
