What is the stack (Stack)?
A stack is an abstract data structure (Abstract Data Type – ADT for short), almost used in almost every programming language. Name the stack because it acts as a stack in real life, such as a deck of cards or a stack of disks, etc.
In real life, the stack only allows operations at the top of the stack. For example, we can only place or add a card or a disk to the top of the stack. Therefore, the abstract data stack structure only allows data manipulation at the top position. At any time, we can only access the top element of the stack.
This feature makes the stack become LIFO format data structure. LIFO stands for Last-In-First-Out. Here, the element placed (inserted, added) will eventually be accessed first. In stack terminology, insert operations are called PUSH operations and delete operations are called POP operations.
Demonstration of stack data structure (Stack)
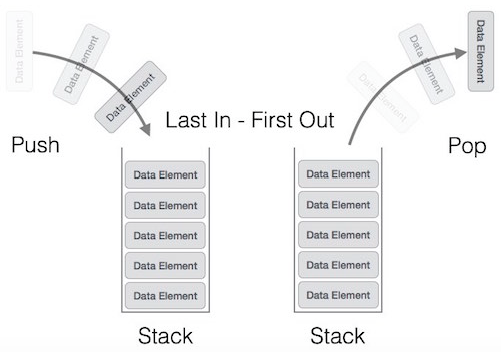
Below is a diagram illustrating a stack and the activities taking place on the stack.
A stack can be deployed by Array method (Array), Structure (Struct), Cursor (Pointer) and Linked List (Linked List). The stack may be in a fixed size or a resizable stack. Below we will deploy the stack using arrays with deployment of fixed stacks.
Basic operations on the stack data structure
The basic operations on the stack may involve initializing the stack, using it and then deleting it. In addition to these basic operations, a stack has two primitive activities related to the concept, namely:
- Push operation () : store an element on the stack.
- Pop () operation : delete an element from the stack.
When the data has been PUSH up on the stack:
In order to use the stack effectively, we also need to check the status of the stack. For this purpose, here are some other support features of the stack:
- Peek () operation : get the data element at the top of the stack, without deleting this element.
- IsFull () operation : check if the stack is full.
- Operation isEmpty () : check if the stack is empty or not.
At all times, we maintain a pointer to the last PUSH data element on the stack. Because this pointer always represents the top position of the stack so is named top . The top pointer gives us the value of the top element of the stack without having to perform the above delete operation (pop operation).
The next section will learn about methods to support stack features.
The peek () method of the stack data structure
The peek () function algorithm:
1 2 3 4 5 | Start the peek function return stack [top] function end |
Deployment of the peek () function in C language:
1 2 3 | int peek () { return stack [top]; } |
The isFull () method of the stack data structure
The algorithm of isFull () function:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 | Start the isfull function if top equals MAXSIZE return true else return false end if function end |
Deployment of isFull () function in C language:
1 2 3 4 5 6 | bool isfull () { if (top == MAXSIZE) return true; else return false; } |
The isEmpty () method of the stack data structure
The algorithm of isEmpty () function:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 | start function isempty if top is less than 1 return true else return false end if function end |
The implementation of isEmpty () function in C language is a bit different. We initialize the top at -1, just like the index of the array starts from 0. So we check if the top is below 0 or -1, the stack is empty. Here is the code:
1 2 3 4 5 6 | bool isempty () { if (top == -1) return true; else return false; } |
PUSH operation in the stack data structure
The process of placing (adding) a new data element on the stack is also known as PUSH Activity. Push activities include the following steps:
- Step 1 : check if the stack is full.
- Step 2 : If the stack is full, the process fails and exit.
- Step 3 : If the stack is not full, increase the top to point to the next available memory.
- Step 4 : Add the data element to the location where the top is pointing to the stack.
- Step 5 : return success.
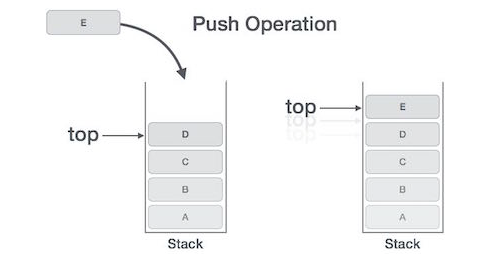
If the Linked List is used to deploy the stack, then in step 3 we need to allocate a dynamic space.
Algorithm for PUSH operation of the stack data structure
The above word can deduce a simple algorithm for PUSH operation in the stack data structure as follows:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 | Start push operation: stack, data if stack is full return null end if top ← top + 1 stack [top] ← data function end |
The implementation of this algorithm in C language is:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 | void push (int data) { if (! isFull ()) { top = top + 1; stack [top] = data; } else { printf ("Don't add to the stack Stack day day"); } } |
To learn the C program fully illustrates the above activities of the stack, please click on the chapter: Stack (Stack) in C.
POP operation of the stack data structure
Accessing element content while deleting it from the stack is also known as POP Activity. In the Array deployment of pop () operation, the data element is not actually deleted, instead the top is reduced to a lower position in the stack to point to the next value. But in the Linked List implementation, the pop () operation actually deletes the data element and deletes it from the memory space.
POP operations may include the following steps:
- Step 1 : check if the stack is empty or not.
- Step 2 : If the stack is empty, the process fails and exit.
- Step 3 : If the stack is not empty, accessing the data element at the top is pointing to.
- Step 4 : reduce the value of the top 1.
- Step 5 : return success.
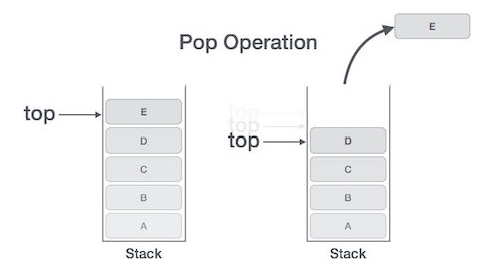
Algorithms for POP operations
From the above we can deduce the algorithm for POP operation on the stack data structure as follows:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 | start pop: stack function if stack is empty return null end if data ← stack [top] top ← top - 1 return data function end |
The implementation of algorithms in C language is as follows:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 | int pop (int data) { if (! isempty ()) { data = stack [top]; top = top - 1; return data; } else { printf ("Khong the lay du lieu, Stack la in."); } } |
To learn the C program fully illustrates the above activities of the stack, please click on the chapter: Stack (Stack) in C.
Tutorial series Our data structure and algorithms are based on: Tutorialspoint
Follow Techtalkvietnam to continue to follow the latest series on Java, C, C ++, Javascript, HTML, Python, Database, Mobile …. Our latest.
