In part 1 , I gave a brief introduction to the TRILEMMA in the block chain, as well as the factors surrounding this issue. The question that most people are probably most interested in is out of the 3 factors Scalability, sercurity, and Decentralization , which is the factor that blockchains are currently interested in or in other words are trading off to achieve the other 2 factors according to TRILEMMA theory? And how do current blockchains solve this problem? For answers to these two questions, please continue reading the content below.
WHAT ARE THE FACTORS THAT MOST OF BLOCKCHAINS ARE CHANGING FOR?
Out of the three Trilemma concepts, scalability is what most blockchains choose to trade off to achieve the other two or in other words one of the main limitations of blockchain at the moment is scalability. wide [1] . This is because decentralization and security are at the core of blockchain technology: Decentralization reflects the fundamental nature of blockchain while security is an absolute requirement.
Blockchain technology is designed according to a distributed model, in which many computers around the globe connect to each other to confirm and manage transactions. Each element in the network is called a node, and each network node manages a copy of the entire blockchain’s transaction history. The decentralization of the blockchain network reflects its nature, where blockchain is valued for its security and availability. The security of the blockchain is the factor that governs all its aspects. That means a blockchain network must ensure that the transactions on it are correctly authenticated and requires the highest level of security methods to ensure there are no external attacks.
A blockchain system can be considered secure if it can prevent or minimize the risk of an attacker modifying blocks in the chain (The acceptable frequency of modified blocks). This ensures that the integrity of the blockchain is protected.
Reality shows that current blockchain platforms are implementing scalability solutions to speed up transaction processing and reduce costs, helping to bring blockchain to more users that are not solutions. increase the security or decentralization of the platform (of course there are some exceptions due to the specificity and intended use of each blockchain, here we are assessing the overall picture and reviewing the platforms big blockchain).
Some impressively highly scalable blockchains such as: Solana is said to be capable of handling 50,000 (tx/s), NEAR blockchain is capable of handling 100,000 (tx/s), Algorand can handle 6,000 (tx/s), tx/s), Binance Smart Chain (BSC) is said to be capable of processing 300 (tx/s)…
However, these numbers are indicative maximums and are subject to change depending on the current state of the network, the number of users, and the number of transactions being performed on the network. Thereby showing us that improving the scalability of the current blockchain is still a big challenge both in research as well as in practical implementation.
HOW DO CURRENT BLOCKCHAINS SOLVE THIS PROBLEM?
Several solutions to the scalability problem have been proposed, Some of the scaling solutions are implemented on-chain (on the blockchain), while some are implemented off-chain (outside of the blockchain). blockchain). In some studies, these string extension solutions are classified into two types [ 1 , 2 ]:
- First layer solutions : sharding , bigger blocks , and DAG…
- Second layer solutions : payment channels, side chains , and Rollup….
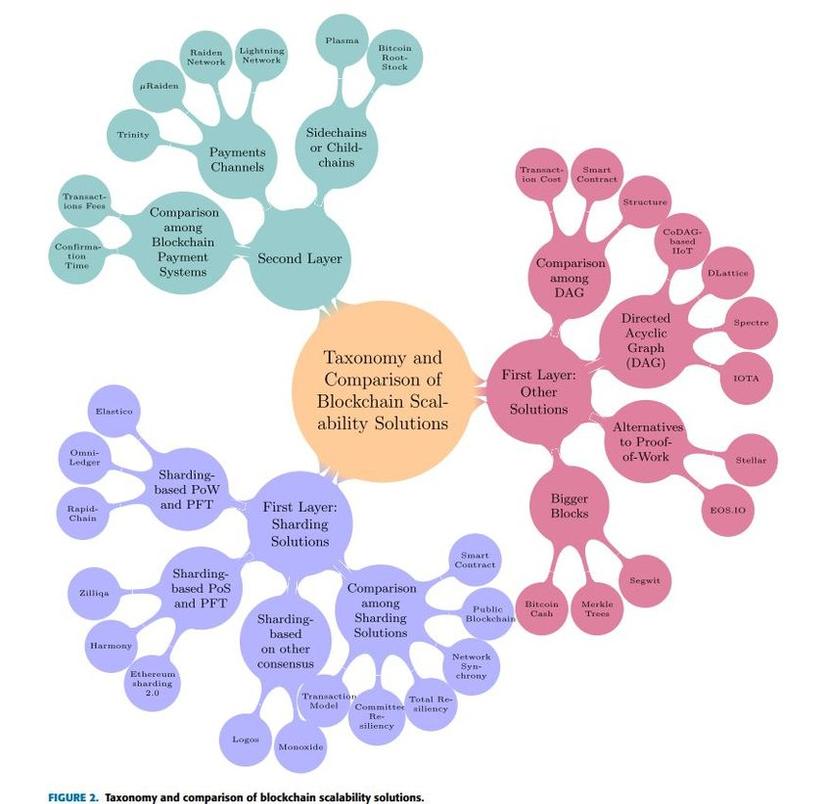
The illustration shows a summary of the classification and comparison of the blockchain scalability solutions that the authors presented in their study [2] . Here in the layer 2 solution, there are still some solutions that the authors have not presented, such as the Rollup solution …. After determining the main problem to be solved of the blockchain at the moment is the ability to solve the problem. With the ability to extend the chain (Scalability), we have to answer a few more important questions before we can dive into what each Layer 1 and Layer 2 solution is.
WHAT ARE THE OBJECTIVES OF CHAIN EXTENSION SOLUTIONS ?
The goal of current blockchain scalability solutions is to process large numbers of transactions per second (i.e. throughput) without sacrificing security and decentralization.
WHAT FACTORS AFFECT THE CHAIN EXTENSION?
Several factors affect blockchain scalability, these factors include: throughput, storage, cost, and latency.
Throughput : Throughput is the number of transactions that the blockchain system can process in a unit of time. With more and more transactions on the blockchain, improving throughput is important to ensure the scalability of the system. Solutions such as new mining algorithms (e.g. Proof of Stake) or increasing the maximum number of blocks per unit time will help improve the throughput of the system.
Storage : The size of each block in the blockchain will grow with the number of transactions being added. Related to that, the data storage capacity of the system will be an important factor affecting the scalability of the blockchain system. Some solutions to reduce storage traffic include the use of data compression protocols (e.g. SegWit) or split blockchains (e.g. sidechains).
Cost: Scaling a blockchain system requires a lot of resource investment, including bandwidth, hardware, and energy. Therefore, cost is an important factor affecting the scalability of a blockchain system. Solutions to reduce costs include the use of new technologies such as the use of special hardware (e.g. ASIC) for mining operations, and the development of cloud partners to reduce server operating costs.
Latency: Latency is the amount of time between when a transaction is sent and when it is confirmed and included in the blockchain. Large latency can cause transactions on the blockchain network to be slow or unconfirmed, affecting system availability and scalability. Solutions such as improving the validation algorithm and solving the problem of increased validation to improve latency can help increase the scalability of the blockchain system.
EXPLAIN SOME CONCEPTS
The acceptable frequency of modified blocks in a blockchain network depends on factors such as desired security, distribution, and size of the network. In practice, different blockchain networks have different safety standards, however, one of the typical standards that has been put forward by Bitcoin is the 6-block standard. The 6-block rule refers to the number of confirmations that are considered secure for a transaction on the Bitcoin network. After a transaction is broadcast to the Bitcoin network, it can be included in a block published to the network. When that happens, it is said that the transaction was mined at 1 block depth. With each subsequent block found, the number of blocks is increased by one. To ensure double spending, a transaction should not be considered confirmed until it reaches a certain number of blocks.
Double spending is an issue where a user tries to spend the same digital currency twice or more. This can lead to a decrease in the value of the digital currency and loss of user confidence. However, Bitcoin solved the double spending problem from the very beginning. Therefore, double spending Bitcoin is not possible.
REFERENCES
[1] Thibault, LT, Sarry, T., & Hafid, AS (2022). Blockchain scaling using rollups: A comprehensive survey. IEEE Access.
[2] Hafid, A., Hafid, AS, & Samih, M. (2020). Scaling blockchains: A comprehensive survey. IEEE Access, 8, 125244-125262.
After understanding the concepts and understanding the factors affecting the scalability of blockchain, will we have a better overview and understanding of each solution that blockchain platforms are applying? In the next articles, I will go into each solution and analyze more deeply the characteristics of these solutions to find out which is the best and available solution. Hope the article is not too long and look forward to receiving everyone’s sharing on this topic. Thank you to everyone who took the time to read this article.
