If OS has a comparison between Windows and Linux, virtualization technology has VMware and KVM. Besides OpenVZ, Hyper-V, two names WMware and KVM (Kernel-based Virtual Machine) are two virtualization technologies that are used more commonly when deploying virtual private servers (VPS). Let’s compare the difference.
I. Brief biography
- VMware, or specifically VMware ESXi, is a virtualization solution of the American software company VMware – a provider of server and virtual machine infrastructure solutions in datacenters.
- KVM is a Linux-based virtual machine technology, developed by Red Hat by Red Hat. At this point, you will also realize that the first and most obvious difference between these two virtualization solutions is that KVM is a free, open source solution. And VMware does not.
So in the end, what is the difference between “company goods” and “open source” really?
II. Detailed comparison
1. Stability
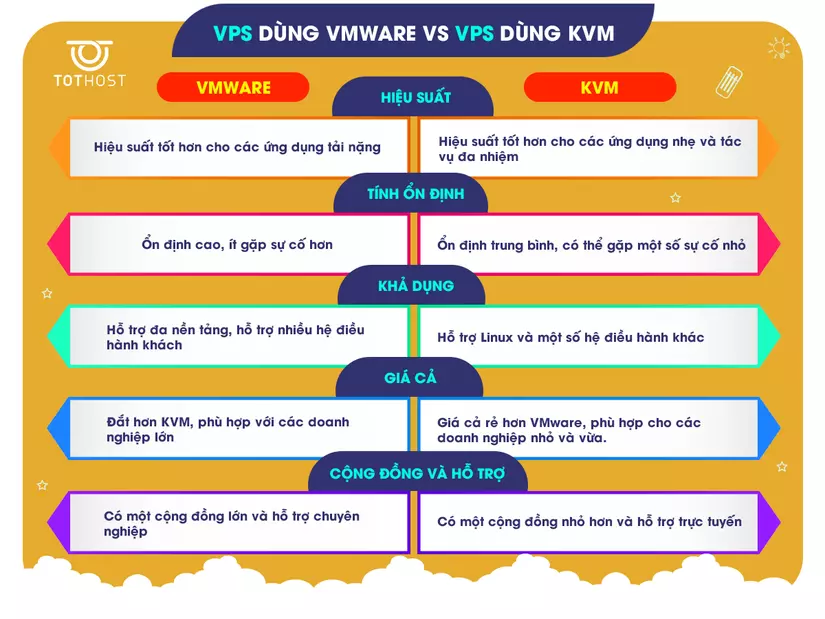
Both VMware and KVM are highly stable. However, VMware’s stability is more appreciated (even, arguably the most stable on the market today). VMware provides tools and support to resolve issues that arise, including virtual machine crash recovery, backup and recovery, and monitoring functionality. The stability of KVM depends on the host operating system. KVM provides virtual machine management tools and monitoring support, but these tools can be more limited than VMware. If something goes wrong, recovery of the virtual machine may take longer than in VMware. However, KVM is highly stable when used on Linux systems.
2. About performance
- CPU and memory performance: handle heavy, resource-intensive tasks, VMware will prevail.
- Virtualization: VMware’s virtualization capacity is higher and latency is lower than that of KVM, thus ensuring smooth and efficient application running.
- Storage features: VMware supports many drive formats, including VMFS (Virtual Machine File System). KVM supports common drive formats like qcow2, raw, etc., but does not support advanced features. like thin provisioning, cloning and snapshot like VMware.
- Network performance: Both provide network virtual machines, load balancing, network partitioning and virtual networks. KVM is built into Linux distributions, it may have some limitations in network management.
- Startup and recovery performance: Overall, VMware boots up and recovers faster. In other words, for environments that require HA & rapid resiliency, WMware prevails. As for common needs: smaller virtualized environments and systems with less complex needs, KVM is still a good solution.
3. Flexibility and Availability
VMware and KVM both have great flexibility in running different applications on virtual machines and can be integrated with different cloud technologies:
- Hardware support: Same support for many hardware and applications. However, KVM does not support specialized features like VMware.
- Management and Deployment: VMware offers vCenter, vSphere, and vRealize. KVM managed through oVirt, Cockpit and Proxmox VE.
- Cross-platform support: Windows, Linux and UNIX
- Cloud support: VMware has VMware vCloud Director and VMware Cloud Foundation. KVM has OpenStack and oVirt.
- Service and community support: VMware supports customers through premium support services. As for KVM, because it’s free, you’ll have to find support via email or on the forum.
- Management interface: In WMware is an intuitive management interface with many management features and extended features. The KVM interface is simple and easy to use. It is built-in to Linux distributions and can be managed remotely.
4. Confidentiality
VMware provides secure virtual machine and virtual network features. KVM also has features for virtualization of devices, firewalls, and user permissions. But compared to VMware, KVM has fewer security features and hasn’t been optimized to meet enterprise needs.
5. Price
As mentioned in the beginning, VMware is a commercial product. VMware’s paid versions cost anywhere from a few thousand to tens of thousands of dollars per year depending on version and features. VMware ESXi is free, but features limited and no technical support. Meanwhile , KVM is a free and open source solution that is included with most Linux distributions, including CentOS, Ubuntu, and Red Hat Enterprise Linux. Therefore, users do not need to pay fees for using KVM.
In short, VMware is a paid product, while KVM is free. However, implementing KVM may require some other overhead. Therefore, choosing between VMware and KVM needs to consider the needs and budget of each individual and business.
The article is long, hopefully this information can help people better understand both virtualization solutions and can make the right choice. Here is an infographic that summarizes the main points: